Understanding the nature of accounts receivable (AR) and its classification is crucial to maintain accurate bookkeeping records. One common question that arises is is accounts receivable a debit or credit? This article will detail the fundamental principles underlying the proper classification of accounts receivable.
Accounts receivable represents a debit entry, indicating the outstanding sum owed to a business by an individual or organization. The amount reflects a financial obligation owed to the business, showing the balance yet to be collected. This makes accounts receivable a debit or credit account that normally carries a debit balance.
There are various instances where debits can arise, representing amounts owed to your business by customers for goods or services. Debits also include compensation owed to you for services rendered, outstanding wages due to employees who received salary advances, and anticipated tax refunds from the IRS.
Conversely, credit accounts receivable can occur when the business owes money to others. For example, credits include taxes your corporation owes, expenses for goods or services received, refunds to customers for returned products, and outstanding wages owed to workers.
What is Accounts Receivables?
AR plays a vital role in business operations by handling the responsibility of collecting funds owed by customers for goods or services provided on credit. Effective management of AR is critical for maintaining healthy cash flow, improving customer satisfaction, and enhancing overall profitability.
Receivables represent outstanding debts clients owe your business for products or services. These receivables are valuable assets and may be used as collateral for loans. In contrast, payables represent debts your company owes to others.
Onboard Customers 5x Faster with AI-powered Credit Automation. Download Your Guide
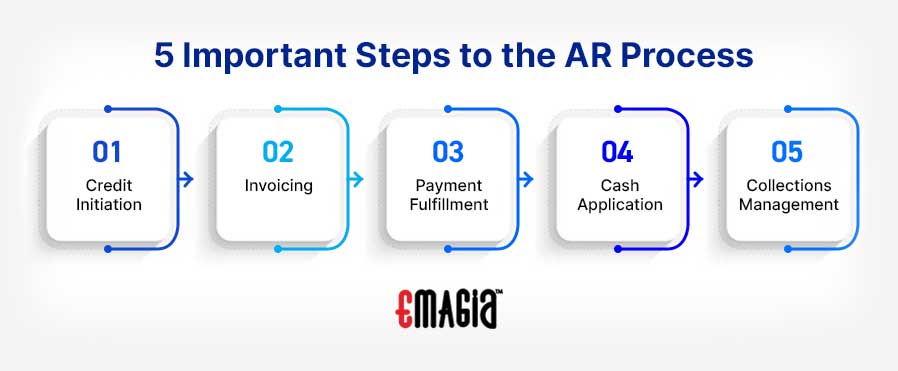
What is the Accounts Receivable Process?
There are 5 important steps to the AR Process:
- Credit Initiation: Extending credit to a client to obtain goods or services now and defer payment.
- Invoicing: Sending the invoice notifying the customer of amount due and payment deadline.
- Payment Fulfillment: Customer remits payment, often streamlined via automated tools in the digital payment process.
- Cash Application: Matching payment received to the invoice in the AR ledger.
- Collections Management: For late payments, initiating collection efforts through notices, late fees, agencies, or legal action using collections management software.
Accounts Receivable Post Raising of Invoices
After delivering products or services, an invoice is generated and cash flow begins. Payment on these invoices keeps trade receivables positive, reflecting an amount the entity expects to receive within the agreed period. These accounts receivable debit or credit entries are recorded as debits and classified as assets on the balance sheet.
Digital B2B Credit Risk Management Best Practices. Download eBook
Accounts Receivables in Case of Advance Payment
When payment is received before goods or services are delivered, invoices follow afterward. In such cases, accounts receivable may show a negative value, indicating a credit balance. This means the entity owes services or goods to the customer. Advance payments are credited, reflecting the obligation to fulfill services.
Accounts Receivable Balance Sheets
What are Credit Terms?
Credit terms define the payment period clients agree to, such as “net 30” or “net 60” days after purchase on credit. Offering discounts for early payment encourages faster cash inflows, improving business liquidity and growth potential.
What is a Credit Balance in AR?
While occasional credit balances in accounts receivable are common, persistent credit balances may indicate issues in billing or collections. Establishing a credit balance policy ensures structured billing and healthy cash flow management.
Conclusion
In summary, accounts receivable represents amounts owed by customers for goods or services on credit. Though it is an asset account, whether it is a debit or credit depends on accounting perspective and double-entry bookkeeping. From the business standpoint, accounts receivable is a debit entry reflecting amounts to be received.
For more insights, visit accounts receivable debit or credit.
FAQs
Why is AR debited?
Because AR is an asset, it is debited.
Can AR be a credit?
If a company owes money to a client, AR can be a credit.
How is AR recorded?
AR is recorded as an asset on the balance sheet.
What kind of account is AR?
AR is considered an asset account.
Are expenses supposed to be debited or credited?
Expenses are usually debited.





